What is Thermal Paste Pump-Out on a CPU and a GPU?
Many of us think that applying thermal paste to the CPU or GPU will always help to increase the heat transfer efficiency. That’s not always the case. We can encounter issues like thermal paste pump-out which can actually bring in a negative set of problems that you need to solve.
Otherwise, you will end up with massive heating issues and that alone is not ok. That’s why you want to know what pump-out is and how you can mitigate its effect. The more you know about it and the faster you find a solution to prevent it, the better the results will be.
What is the pump-out effect on a CPU and a GPU?
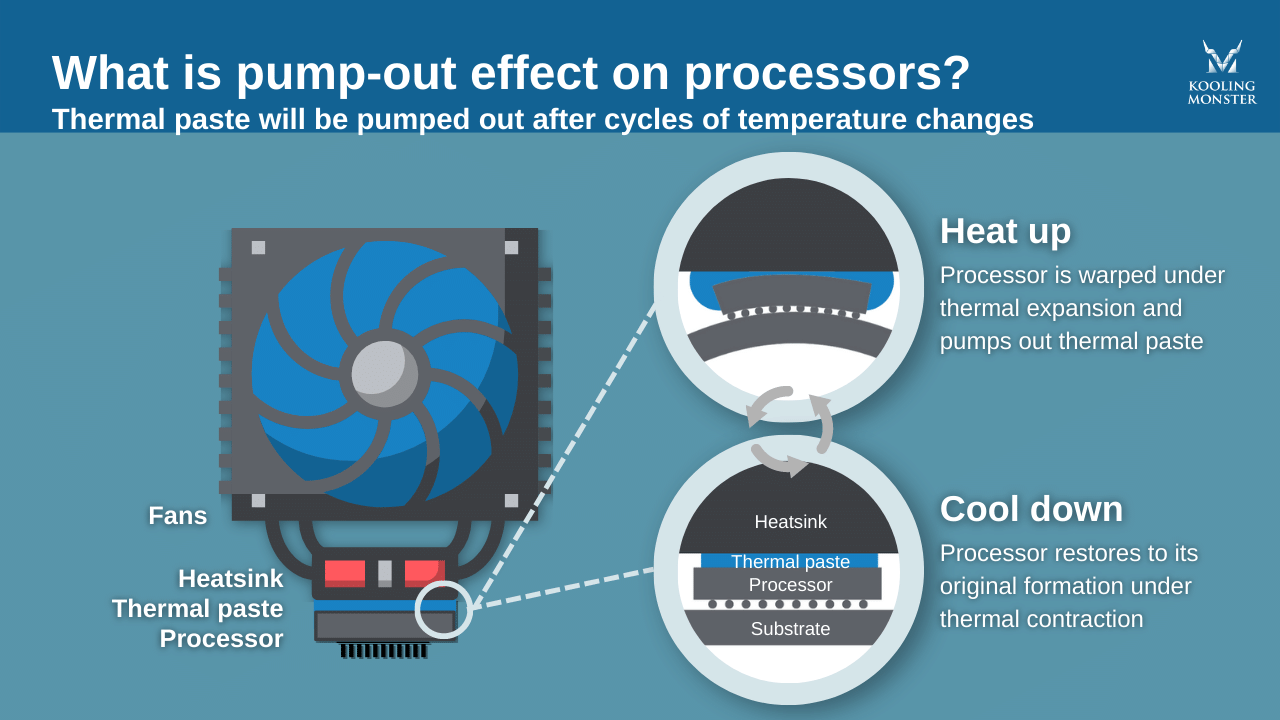
Simply put, pump-out means that the thermal paste gets pumped out from the central processor. This happens when there are temperature changes, and the substrate and processor get warped at the microscopic level, and they gradually move that thermal paste outward. Generally, the processor will have many cycles where it heats up, then it cools down.
The pump-out process continues, and eventually you will not have any thermal paste in the central part of the processor. What this does is it leads to a higher processor temperature. Not only that, but the heat transfer efficiency is lower, so your processor will only get hotter and hotter as time goes by.
When do we have temperature changes? Generally, you have these when you use the computer to do intensive tasks. Videogames are a great example here, because the CPU or GPU gets very hot during this time, and then it cools down when you stop playing the game. Even running various programs can lead to pump-out. All these things are normal for us, but the processor has to deal with these heat and cooling cycles and those can have a negative impact on the process. That’s why you want to know when you have to replace the thermal paste and how to do it. (Learn more about How to Apply Thermal Paste to a CPU? [2022 Step-by-Step Beginner Guide])
What kinds of CPUs and GPUs lead to pump out?
The thing to keep in mind is that processors are usually impacted by the pump-out process in a different manner. For example, if you have a processor with lid, it will have less pump-out effect when compared to a processor without lid.
Processor with lid
The role of a lid is to shield and protect processors. This is designed to distribute heat from the processor itself to a CPU cooler, as well as provide protection to the processor inside. If your processor doesn’t have a lid, and it just has a naked die or bare die, then that means heat transfer efficiency is improved because a lid could be an extra barrier that heat needs to pass through. However, without a lid, processor directly contacts heat sink, leading to the pump-out effect.
Generally, all current desktop Intel and AMD CPUs have a lid, which is great because it adds a lot of value and protection to the unit. Lids help mitigate that pump-out effect, but slightly decrease heat transfer efficiency from processor to heatsink
Processor without lid
Though, not all processors have a lid. Some of them, like a laptop CPU, the GPU or the console CPUs don’t really have a lid, and that can be an issue. If there’s no lid on the processor, then the thermal paste will end up facing this pump-out effect from the processor. That becomes a huge issue in the long run. It’s one of the reasons why console processors can overheat quite a bit, and that’s definitely a thing to take into consideration as much as possible here.
Does my thermal paste on the CPU or GPU have pump-out problem?
Trying to figure this out is a very good idea, since it can narrow down what you need to do and how you can solve the problem. For the most part, the desktop CPUs won’t have major pump-out issues, if any at all. They have lids under the current design in both AMD and Intel, so they are protected against overheating and other issues like that.
But on GPUs, laptops, and PS4 CPUs, you will have pump-out issues. The amount of pump-out problems will vary based on what kind of tasks you are performing here. For the most part, you don’t need to worry that much. It can take months or years until pump-out becomes a problem. If you choose to re-apply thermal paste often, you should be more than okay.
How to better prevent the pump-out effect?
What you will notice is that the thermal contraction and expansion happens naturally. You can’t really avoid this on a bard die, a processor without lids. But there are 2 potential mitigation solutions you can take into consideration.
A good idea is to use liquid metal thermal paste. After using it for a while, it automatically forms a protection bar in the outer part of the thermal paste, and that will prevent it from leaking the processor. The downside is that liquid metal thermal paste is electrically conductive, so you can end up damaging your device, which is obviously the thing to avoid. In addition to that, if you do not reapply thermal paste periodically, liquid metal thermal paste might fuse the interface of your processor and heat sink.
Another option is to use the KOLD-01 thermal paste. This one comes with a unique rheological design, and the paste becomes more solid without applying any force. If you apply extra force, the paste becomes fluid. Since it’s more solid than regular thermal paste when no extra force is applied, this option can help to mitigate the pump-out effect. It has a viscosity with spreading force of 100Pa-s and viscosity without spreading force of 1,200Pa-s. What this shows is that the force does make a difference.
The pump-out effect is one of those things that a lot of people are worried about. If you have a desktop CPU, chances are that you don’t really have to worry about the pump-out effect that much because the current desktop CPU designs always have a lid on a processor. If the processor doesn’t have a lid, just like the GPU, PS4 CPU or laptop CPU, then you do need to take some action. It’s better if you just replace the thermal paste once in a while, and you can prevent pump-out. (Learn more about How Often Should You Replace Thermal Paste?)
As we mentioned above, the KOLD-01 thermal paste is the best option to keep in mind if you want to prevent the pump-out effect. It’s designed to be efficient and reliable, and it allows you to focus on the process and ensure everything is working as expected.